Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Polygon PoS
Polygon PoS
Badges
About
Polygon PoS is an EVM-compatible, proof of stake sidechain for Ethereum, planning to become a Validium with a state validating bridge. The bridge is currently validated by Polygon validators and allows for asset as well as data movement between Polygon and... Ethereum.
Badges
About
Polygon PoS is an EVM-compatible, proof of stake sidechain for Ethereum, planning to become a Validium with a state validating bridge. The bridge is currently validated by Polygon validators and allows for asset as well as data movement between Polygon and... Ethereum.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a proper proof system fully rely on single entities to safely update the state. A malicious proposer can finalize an invalid state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Feb 03 — 2026 Feb 03
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Feb 03 — 2026 Feb 03
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Heimdall v2 upgrade
2025 Jul 10th
Major consensus upgrade replacing Heimdall v1 with Heimdall v2.
Funds can be stolen if
- destination token contract is maliciously upgraded,
- a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL),
- validators decide to mint more tokens than there are locked on Ethereum thus preventing some existing holders from being able to bring their funds back to Ethereum,
- validators submit a fraudulent checkpoint allowing themselves to withdraw all locked funds.
Users can be censored if
Users can submit transactions to an L1 queue, but can’t force them. The sequencers cannot selectively skip transactions but can stop processing the queue entirely. In other words, if the sequencers censor or are down, they are so for everyone. In Polygon PoS, the sequencers network corresponds to the PoS validators network, which is composed of 104 members.
Currently the system permits invalid state roots. More details in project overview.
Data is guaranteed to be available by an external proof of stake network of validators. On Ethereum, DA is attested via signed block headers.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
The PoS network is composed of 104 validators. Blocks are included in the chain only if signed by 2/3+1 of the network stake. It’s currently not possible to join the set if the validator cap is reached. The current validator cap is set to 105. In the event of a failure in reaching consensus, withdrawals are frozen.
State updates are settled on Ethereum if signed by at least 2/3+1 of the Polygon PoS validators stake. Contracts on Ethereum do not check whether the state transitions are valid.
Users can be censored if validators on Polygon decide to not mint tokens after observing an event on Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if validators decide to mint more tokens than there are locked on Ethereum thus preventing some existing holders from being able to bring their funds back to Ethereum.
Funds can be stolen if validators submit a fraudulent checkpoint allowing themselves to withdraw all locked funds.
Destination tokens are upgradeable
Tokens transferred end up as wrapped ERC20 proxies, some of them are upgradable. The contract is named UChildERC20Proxy.
Funds can be stolen if destination token contract is maliciously upgraded.
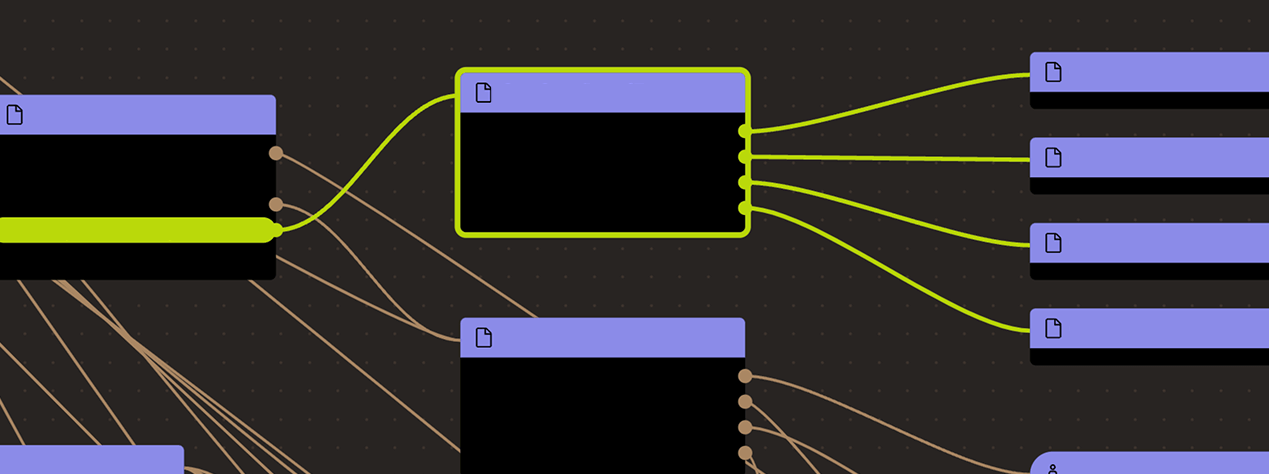
Ethereum
Actors:
A Multisig with 5/9 threshold. Can propose and execute code upgrades. Can arbitrarily moves tokens out of the ERC20 escrow without a contract upgrade.


Ethereum
Contract storing Polygon PoS chain checkpoints. Note that validity of these checkpoints is not verified, it is assumed to be valid if signed by 2/3 of the Polygon Validators.
Smart contract allowing whitelisted addresses to send messages to contracts on Polygon PoS chain.
Main configuration contract to manage tokens, token types, escrows (predicates) for given token types. It also serves as an entry point for deposits and withdrawals effectively acting as a token router.
Main configuration contract to manage stakers and their voting power and validate checkpoint signatures.
Contains logging and getter functions about staking on Polygon.
Maintains the addresses of the contracts used in the system.
Contract to deposit and escrow ETH, ERC20 or ERC721 tokens. Currently only used for POL.
- This contract can store any token.
Contract handling users’ withdrawal finalization for tokens escrowed in DepositManager.
Contract used to initiate ERC20 token withdrawals. The function to handle Plasma proofs is empty, meaning exits cannot be challenged.
Contract used to initiate ERC721 token withdrawals. The function to handle Plasma proofs is empty, meaning exits cannot be challenged.
Contains events used by other contracts in the system.
NFTs used to represent a withdrawal in the withdrawal PriorityQueue (Only used for tokens initially deposited via DepositManager).
Contract enforcing delay on code upgrades. The current delay is 0s.
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
